Ray to Octree Intersection for boolean geometry
In case you have posted some images, they do not show at least for me. All posts are empty:
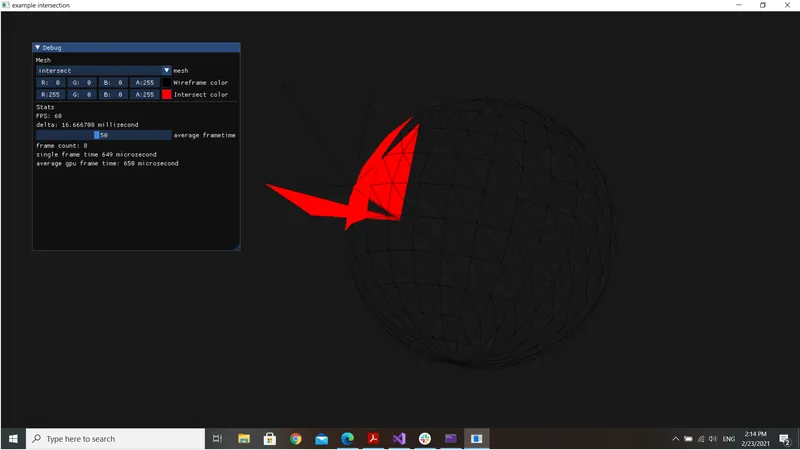
These are very weird result, I don't know I'm very upset and don't know how to proceed, here is my current code
auto tri_mesh_a = cg::trimesh_from_indexed_mesh(sphere_indexed_mesh);
auto tri_mesh_b = cg::trimesh_from_indexed_mesh(cube_indexed_mesh);
auto octree_a = cg::octree_from_mesh(tri_mesh_a);
auto octree_b = cg::octree_from_mesh(tri_mesh_b);
std::stack < cg::Octant*> stack;
int inx = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < tri_mesh_a.vertices.count; i+=3)
{
musa::Triangle triB{ tri_mesh_a.vertices[i], tri_mesh_a.vertices[i + 1], tri_mesh_a.vertices[i + 2] };
vec3 a_e1 = triB.p1 - triB.p0;
vec3 a_e2 = triB.p2 - triB.p0;
vec3 normalA = normalize(cross(a_e1, a_e2));
stack.push(octree_b.root);
while (!stack.empty())
{
cg::Octant* node = stack.top();
stack.pop();
if (box_box_intersect(musa::triangle_bounding_box(triB), node->region))
{
auto vertices = node->faces;
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.points, triB.p0);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.indices, inx++);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.points, triB.p1);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.indices, inx++);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.points, triB.p2);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.indices, inx++);
for (size_t j = 0; j < vertices.count; j +=3)
{
musa::Ray ray;
ray.origin = { vertices[j] };
ray.dir = { 1,0,0 };
musa::Triangle triA{ vertices[j], vertices[j + 1], vertices[j + 2] };
musa::Intersection_Points t = musa::ray_triangle_intersection(ray, triB);
if (t.count == 1)
{
vec3 dir = { normalA};
float tdot = dot(normalize(t.points[0]), dir);
if (tdot > 0 && tdot <= 1)
{
vec3 p1 = musa::lerp(triB.p0, triA.p0, tdot);
vec3 p2 = musa::lerp(triB.p1, triA.p1, tdot);
vec3 p3 = musa::lerp(triB.p2, triA.p2, tdot);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.points, p1);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.points, p2);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.points, p3);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.indices, inx++);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.indices, inx++);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.indices, inx++);
}
}
}
for (auto& n : node->octants)
{
if (n == nullptr)
continue;
stack.push(n);
}
}
}
}
AhmedSaleh said:
These are very weird result, I don't know I'm very upset and don't know how to proceed, here is my current code
I'm working on geometry for years, and i can relate : )
You have too much on your plate. As proposed before, make a test setup with only two intersecting triangles and work on tessellation in isolation.
I refactored the code, now getting the triangles that are interesting, not included, a bug is there, don't know where is the problem.
Would you take some time look at it please ?
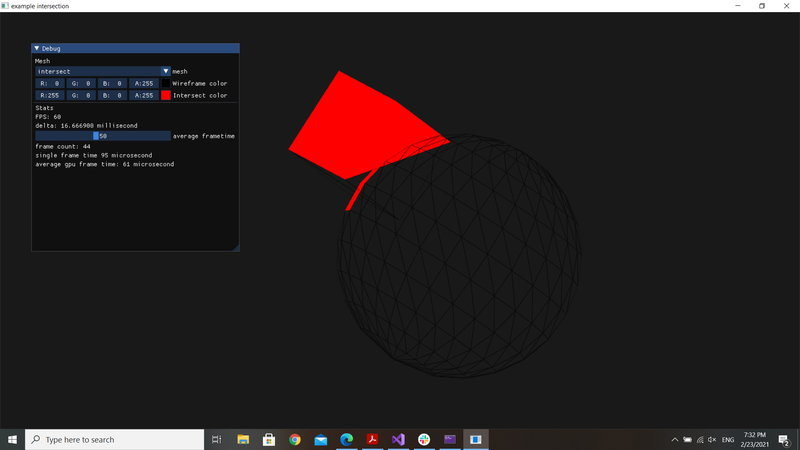
auto t1 = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto tri_mesh_a = cg::trimesh_from_indexed_mesh(sphere_indexed_mesh);
auto tri_mesh_b = cg::trimesh_from_indexed_mesh(cube_indexed_mesh);
auto octree_a = cg::octree_from_mesh(tri_mesh_a);
auto octree_b = cg::octree_from_mesh(tri_mesh_b);
std::stack < cg::Octant*> stack;
int inx = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < tri_mesh_a.vertices.count; i += 3)
{
musa::Triangle triA{ tri_mesh_a.vertices[i], tri_mesh_a.vertices[i + 1], tri_mesh_a.vertices[i + 2] };
musa::Ray ray;
vec3 a_e1 = triA.p1 - triA.p0;
vec3 a_e2 = triA.p2 - triA.p0;
vec3 normalA = normalize(cross(a_e1, a_e2));
ray.origin = { tri_mesh_a.vertices[i] };
ray.dir = { normalA };
stack.push(octree_b.root);
while (!stack.empty())
{
cg::Octant* node = stack.top();
stack.pop();
if (box_box_intersect(musa::triangle_bounding_box(triA), node->region))
{
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.points, triA.p0);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.indices, inx++);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.points, triA.p1);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.indices, inx++);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.points, triA.p2);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.indices, inx++);
for (size_t k = 0; k < tri_mesh_b.vertices.count; k += 3)
{
musa::Triangle triB{ tri_mesh_b.vertices[k], tri_mesh_b.vertices[k + 1], tri_mesh_b.vertices[k + 2] };
musa::Intersection_Points t = musa::ray_triangle_intersection(ray, triB);
if (t.count == 1)
{
vec3 dir = { 1,0,0 };
float tdot = dot(normalize(t.points[0]), dir);
if (tdot > 0)
{
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.points, triB.p0);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.points, triB.p1);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.points, triB.p2);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.indices, inx++);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.indices, inx++);
mn::buf_push(self->modelIntersection.indices, inx++);
}
else
{
}
}
}
for (auto& n : node->octants)
{
if (n == nullptr)
continue;
stack.push(n);
}
}
}
}AhmedSaleh said:
I refactored the code, now getting the triangles that are interesting, not included, a bug is there, don't know where is the problem. Would you take some time look at it please ?
I realize your intersection function seeks for intersection by tracing rays along the normal, but that's likely not working.
A proper intersection test would be:
Calculate the intersection of both triangle planes, which is a infinite line.
Then clip that line by all edges from both triangles.
A great resource for intersection tests is this library: https://www.geometrictools.com/ I guess it has tri-tri as well.
Can you please tell me the algorithm for clipping lines ? for example If I have a function that calculates the triangle triangle intersection and result in segments, what should I do with that ?
AhmedSaleh said:
for example If I have a function that calculates the triangle triangle intersection and result in segments, what should I do with that ?
I don't know what ‘segments’ you get - you should know yourself.
However, i found this in my code. Pretty sure i have ported this this from Dave Eberlys source linked above. And i might have used this only to try something out, so i'm not sure how buggy this is.
inline float IntersectRayPlane (qVec3 &rO, qVec3 &rD, qVec3 &pO, qVec3 &pN)
{
// rD does not need to be unit length
float d = pN.Dot(rD);
float n = pN.Dot(pO - rO);
if (fabs(d) < FP_EPSILON) // ray parallel to plane
{
if (fabs(n) < FP_EPSILON) return 0; // ray lies in plane
else return FLT_MAX; // no intersection
}
float t = n / d;
//sVec3 intersectionPoint = rP + rD * t;
return t;
}
inline int IntersectPlanePlane (qVec3 &interPos, qVec3 &interDir,
qVec3 &mPlane0, qVec3 &mPlane1)
{
// If N0 and N1 are parallel, either the planes are parallel and separated
// or the same plane. In both cases, 'false' is returned. Otherwise,
// the intersection line is
// L(t) = t*Cross(N0,N1)/|Cross(N0,N1)| + c0*N0 + c1*N1
// for some coefficients c0 and c1 and for t any float number (the line
// parameter). Taking dot products with the normals,
// d0 = Dot(N0,L) = c0*Dot(N0,N0) + c1*Dot(N0,N1) = c0 + c1*d
// d1 = Dot(N1,L) = c0*Dot(N0,N1) + c1*Dot(N1,N1) = c0*d + c1
// where d = Dot(N0,N1). These are two equations in two unknowns. The
// solution is
// c0 = (d0 - d*d1)/det
// c1 = (d1 - d*d0)/det
// where det = 1 - d^2.
float dot = mPlane0.Dot(mPlane1);
if (fabs(dot) >= 1.0f - FP_EPSILON)
{
// The planes are parallel. Check if they are coplanar.
float cDiff;
if (dot >= 0)
{
// Normals are in same direction, need to look at c0-c1.
cDiff = mPlane0[3] - mPlane1[3];
}
else
{
// Normals are in opposite directions, need to look at c0+c1.
cDiff = mPlane0[3] + mPlane1[3];
}
if (fabs(cDiff) < FP_EPSILON)
{
// Planes are coplanar.
return COPLANAR;
}
// Planes are parallel, but distinct.
return DISTINCT;
}
float invDet = ((float)1)/((float)1 - dot*dot);
float c0 = (mPlane0[3] - dot*mPlane1[3])*invDet;
float c1 = (mPlane1[3] - dot*mPlane0[3])*invDet;
interPos = c0*mPlane0 + c1*mPlane1;
interDir = qVec3(mPlane0.Cross(mPlane1)).Unit();
return INTERSECT;
}If you give one vertex and normal for each triangle, the second function should return direction and a position on the infinite intersection line. Notice my code is confusing: qVec3 mPlane0 stores the plane equation which are 4 numbers (0,1,2: normal and 3: distance to origin). My qVec3 has 4 values for padding, so i can do this but it's ofc. bad practice.
Then you only need to clip the line with edge planes made from triangle.normal.Cross(triangle.v1 - triangle.v0).





