- overview of architecture
- multiple render backends are supported at the same time
- all GPU resources are referred to by a handle, resources can exist on multiple GPUs
- overview of the high-level command system that is recorded and translated into native API command buffers
- render graph system graph construction and execution
- how to deal with multiple GPUs
- virtual GPU system allows emulation of a multi GPU setup using a single GPU
- proxy backend routes rendering calls to a remote machine for execution
- a brief look at machine learning in a render graph architecture
- overview of the asset pipeline
- overview of hybrid rendering pipeline and how transparent shadows have been implemented using DirectX Raytracing
- discussing open problems with ray tracing

- a new shading language, designed for use with WebGPU
- discusses the constraints of targeting the web, and the ability to convert to Metal, HLSL, and SPIR-V
- SPIR-V limitations also limit the expressiveness of WHLSL
- memory safety for arrays, getter and setter support
- does not support a preprocessor but instead uses a two-pass compilation model with specialization constants
- bindless binding model is not supported
- part 2 of the series on font rendering
- shows the artifacts a regular grid sampling pattern causes and how a rotated grid improves the edges of glyphs that contain straight lines
- explains how to sample the grid efficiently by splitting the rotation into one horizontal and one vertical skew
- able to optimize the sampling by precalculating lookup tables

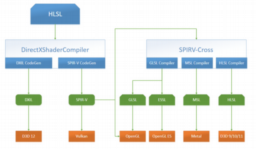
- new open source library from Microsoft that combines the DirectXShaderCompiler and SPIRV-Cross to convert HLSL shaders into OpenGL/Metal/SPIR-V or HLSL compatible with D3D11
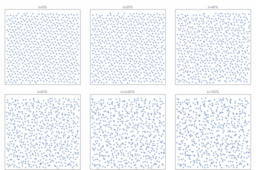
- presents an approach to generate a quasirandom blue noise point sequence
- shows the mathematical foundation, distribution analysis and comparison with other techniques
- python code is provided to help with the understanding of the technique
- podcast episode discusses how to design a cross-platform API, problems, and considerations
- engine design is aimed at modern APIs, supporting older APIs is not a concern for “Our Machinery”
- reverse engineering the sharpening filter from The Witcher 3 and explains how it works step by step
- provides HLSL source code that produces the same assembly

- shows that using DXGI functionality can be used to keep track of Vulkan memory usage on Windows
- presents how to identify physical adapters between Vulkan and DXGI to deal with multi-GPU systems
- experiments with using DXGI for memory reporting when using Vulkan
- results are presented for the system using one AMD and one NVIDIA GPU
- memory management behavior seems to be different between the vendors
- DXGI appears to be able to report sensible application local memory usage information
- the extension allows the application to collect timing information from the presentation engine and schedule presents at specified times
- the post presents results from experimenting with VK_GOOGLE_display_timing on Android and Mesa (X11)
- list of issues encountered and possible points of improvement
- explains how ray-tracing could be used for arbitrary data-lookup in 2D and 3D
- can handle more data points where the signal changes more rapidly
- a texture has a fixed resolution and cannot adjust to varying density needs
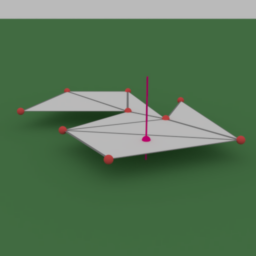
- shows how to generate a depth pyramid for Vulkan
- takes the depth buffer and produces a conservative mipmap chain
- preparation for GPU occlusion culling in the next episode

- implementation of GPU occlusion culling into the mesh-shader and classical rendering pipeline
- list of resources for beginners that are looking to get started with graphics programming
- new Vulkan extension that allows usage of the C++ memory layout in Vulkan constant and structured buffers
- this relaxes the alignment requirements
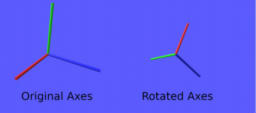
- presents how to recover the scale, rotation, and position from a model matrix
- rotation is retrieved as a rotation matrix
- a presentation about the development and design of a C++ library implementation that allows GLSL shaders to run on the CPU
If you are enjoying the series and getting value from it, please consider supporting this blog.
Support this blog
